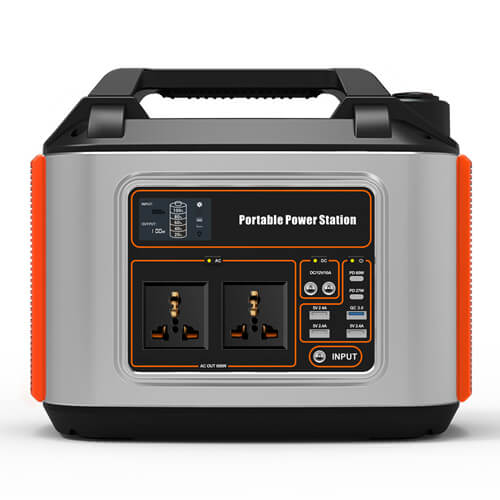
If the lithium battery is overcharged, continuing to charge when the battery is full will lead to the structural change of the cathode material, resulting in capacity loss, and its decomposition and oxygen release will have a violent chemical reaction with the electrolyte, and the worst result is naturally an explosion.
After the lithium battery has discharged the internal stored electricity and the voltage reaches a certain value, continuing to discharge will cause over discharge. Usually, the discharge cut-off voltage is determined according to the discharge current. 0.2c-2c discharge is generally set to 1.0v/ piece, and over 3C discharge such as 5C or 10C discharge is set to 0.8v/ piece. Battery over discharge may bring disastrous consequences to the battery, especially high current over discharge or repeated over discharge have a greater impact on the battery.Generally speaking, over discharge will increase the internal pressure of lithium battery, and the reversibility of positive and negative active substances will be destroyed. Even if charged, it can only be partially recovered, and the capacity will also be significantly attenuated. The deeper the charge and discharge of the lithium battery, the greater the loss of the battery. The ideal state of the lithium battery is shallow charge and shallow discharge. In that case, the longer the battery life.
.jpg)